What Two Word Term Describes a Population Disease Resistance
Populations at one point in time or one population at two or more points in time. In nature population size and growth are limited by many factors.

When Will Covid 19 Go From Pandemic To Endemic World Economic Forum
The two simplest models of population growth use deterministic equations equations that do not account for random events to describe the rate of change in the size of a population over time.

. Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process. Pandemic is also used as a noun meaning a pandemic disease. Theyre named for the distinctive crown-like spikes on the virus surface.
The most frequently used. For example the incidence of thyrotoxicosis during 1982 was 10100 000year in Barrow-in-Furness compared with 49100 000year in Chester. Some polymorphisms can change your susceptibility or resistance to disease.
The resistance of a group to invasion and spread of an infectious agent based on the resistance to infection of a high proportion of individual members of the group. Tx is replacment therapy for antibodies antibiotics for infections. Plant disease resistance protects plants from pathogens in two ways.
As a result of drug resistance antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines become ineffective and. Demur objection protest remonstrance. The incidence of a disease is the rate at which new cases occur in a population during a specified period.
Density-dependent limiting factors cause a populations per capita growth rate to changetypically to dropwith increasing population density. Tx is balance of rest and moderate activity anti-inflammatory drugs heatcold splinting positioning xrays. By pre-formed structures and chemicals and by infection-induced responses of the immune system.
Discussions of population health involve many terms such as outcomes disparities determinants and risk factors which. The terms starting zone track and runout zone are. The WHO more specifically defines a pandemic as a worldwide spread of a new.
When the population at risk is roughly constant incidence is measured as. The resistance can occur naturally but may be enhanced in a population by ARTIFICIAL SELECTION as in plant and animal breeding -for example the breeding of varieties of tomatoes resistant to the fungal disease that. The resistance is a product of the number susceptible and the probability that those who are susceptible will come into contact with an infected person.
Whose presence excessive presence or in deficiency diseases relative absence is essential for the occurrence of a disease. The ability of some organisms to withstand the attack of PATHOGENS and remain virtually unaffected. Human coronaviruses were.
Antimicrobial Resistance AMR occurs when bacteria viruses fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread severe illness and death. One example is competition for limited food among members of a. A growing number of infections such as pneumonia.
There is debate sometimes heated about whether population health and public health are identical or different. What two-word term describes a populations disease resistance that is achieved by either exposure and recovery or an effective vaccine. Population health is a relatively new term with no agreement about whether it refers to a concept of health or a field of study of health determinants.
Antibiotic resistance can affect anyone of any age in any country. Compared to an epidemic disease a pandemic disease is an epidemic that has spread over a large area that is its prevalent throughout an entire country continent or the whole world. Natural variations in a gene DNA sequence protein or chromosome that do not affect the functioning of the gene or cause disease and occur with fairly high frequency in the general population.
Surviving for long periods of time outside the body and must be resistant to drying. At least 144 publications used the term comorbidity without referring to an index disease. Loss of function of one or more components of immune system.
Thirteen general definitions of multimorbidity were identified but only two were frequently used 91 of publications. 1 Introduction of the agent into a new host population whether the pathogen originated in the environment possibly in another species or as a variant of an existing human infection followed by 2 establishment and further dissemination. I have suggested that infectious disease emergence can be viewed operationally as a two-step process.
A situation in which a sufficient proportion of a population is immune to an infectious disease through vaccination andor prior illness to make its. Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health food security and development today. The first of these models exponential growth describes populations that increase in numbers without any limits to their growth.
Comorbidity was used in 67557 publications multimorbidity in 434 and the other terms in three to 31 publications. Some are density-dependent while others are density-independent. Relative to a susceptible plant disease resistance is the reduction of pathogen growth on or in the plant and hence a reduction of disease while the term disease tolerance describes plants that exhibit.
Diagnosis is synovial fluid analysis. Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause a variety of diseases in humans and animals.

What Is Bacteria Good Vs Bad Benefits And Common Types

What Is Bacteria Good Vs Bad Benefits And Common Types

Biodiversity Definition Facts Britannica
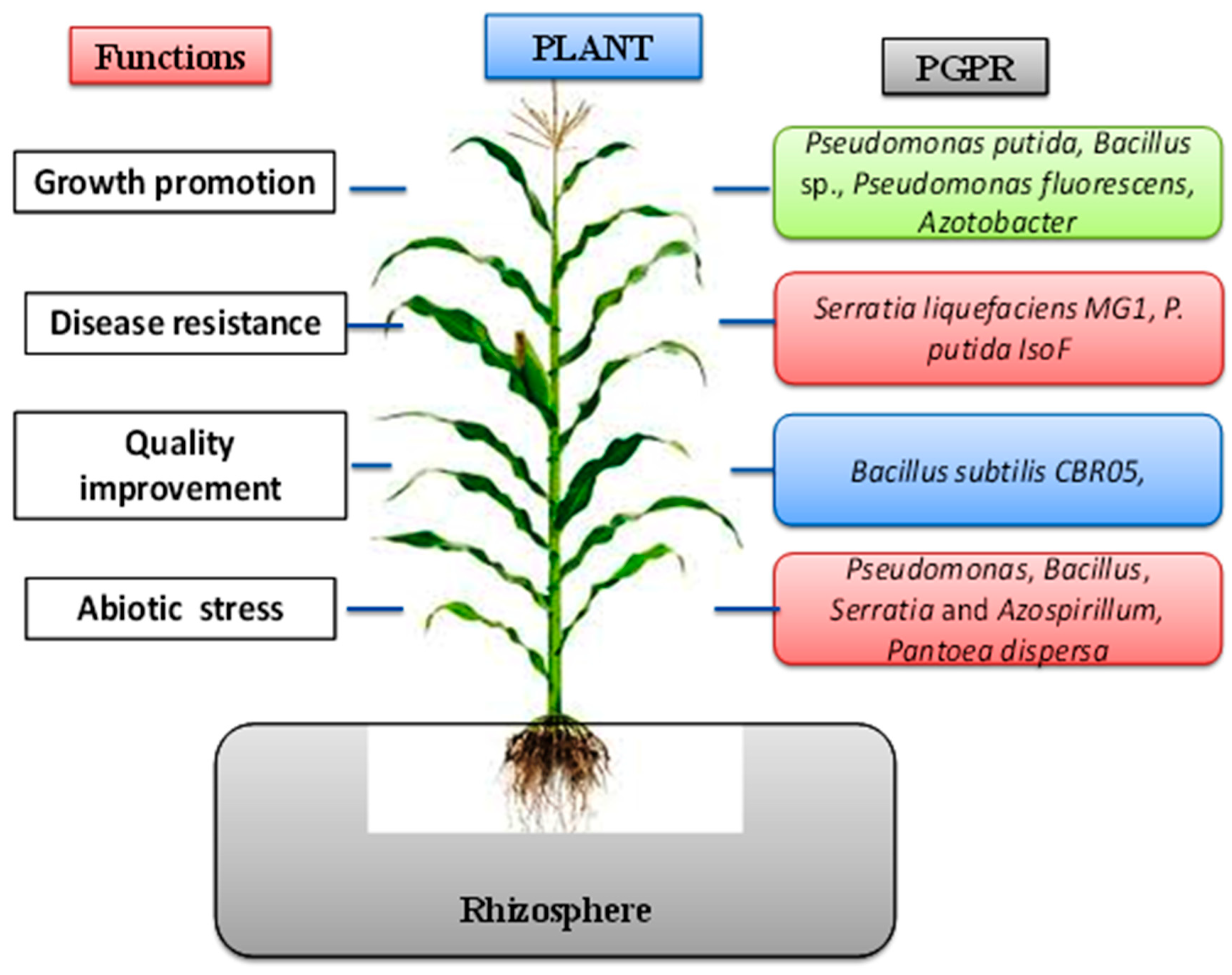
Sustainability Free Full Text Bacterial Plant Biostimulants A Sustainable Way Towards Improving Growth Productivity And Health Of Crops Html
No comments for "What Two Word Term Describes a Population Disease Resistance"
Post a Comment